What does the future of Telecom Industry look like?
It took more than 70 years for Landline to get mass adoption & build the base for the telecom industry. It'll take less than 5 for Starlink to disrupt telecom.
Hey there! Thanks for being a great audience. 🎉
This Sunday, I’m talking about the future of telecom. I enjoyed writing this one, do take your time to think while you read it :)
Before we get started, a quick word on what I’m working on: I’m building Pesto. We help experienced developers get access to global opportunities along with some training.
If you’re a developer looking to join Pesto, let me know here.
If you’re looking to hire a developer, apply for access here.
We send books & merch to random applicants each month & we may reach out for details. Let’s get started :)
The year is 1973, Martin Cooper, then head of the communications systems division at Motorola called Dr. Joel S. Engel, his competitor at AT&T saying “Joel, this is Marty. I’m calling you from a cell phone, a real handheld portable cell phone.” That was the first-ever cell phone call that was made.
Cooper, now considered as the father of the cell phone led the team that developed the first-ever commercially available cell phone, Motorola DynaTAC. The call was made using its prototype that weighed almost 2 Kg, took 10 hours to charge providing 20-30 minutes of talk time!
And how the tables have turned in half a century! We have cell phones that weigh 10 times less, take 30 minutes to charge, and provide 10 hours of talk time. Watch Cooper’s BBC interview here.
Technological innovations have largely shaped the telecommunications industry, today, the global telecom market has over 5 billion smartphones and unique subscribers, with revenues around 5 trillion dollars globally. The number of internet users is expected to rise from 3.7 in 2019 to 5 billion by 2025 (Source: GSMA).
The telecom industry is expected to see a revolution of sorts in the coming years with trends like 5G, AI, Internet of Things (IoT), digital transformation, etc. As 2020 ends, the industry would see more changes happening in the next 5 years than in the past 50.
While these technological advancements present a lot of opportunities, they also come with their own set of challenges that the telecom industry needs to tackle. In this issue, I’ll talk about the trends that are going to reshape the industry and the challenges that it needs to tackle.
Forecasts predict a higher number of mobile network connections and increased smartphone adoption in the future, but there is more to these numbers than that. These projections require telecom operators to plan and expand their operations and make infrastructural changes to solve challenges that come with technological advancements.
Lightning-fast networks and digital applications open the possibility for telecom providers to develop innovative and highly personalized subscriber experiences with ultra-fast response times and seamless connectivity.
Disruptors for the present and future
5G
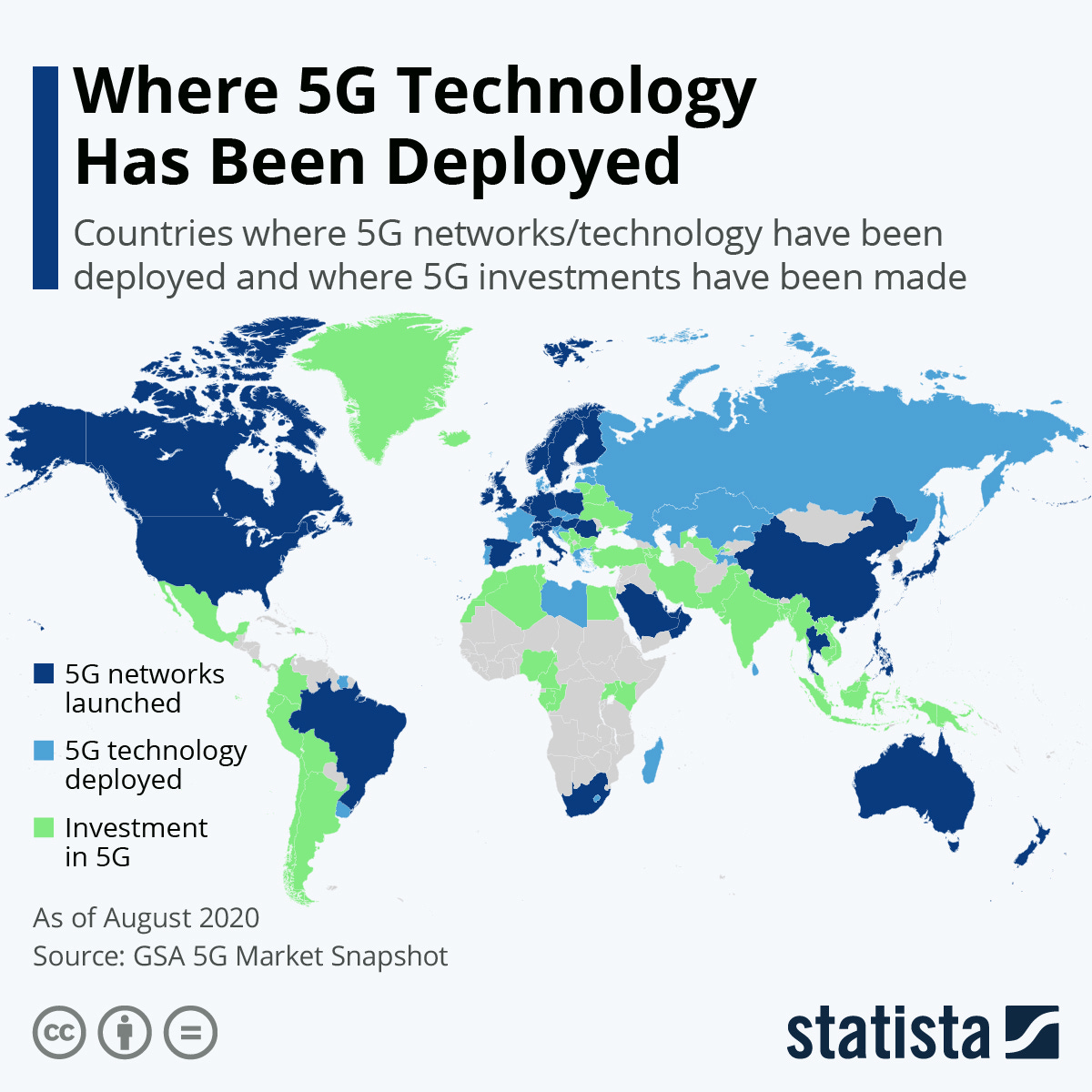
Perhaps the most talked-about technology in the telecom industry right now, 5G is the fifth generation telecommunication standard that promises to bring unprecedented speeds, ultra-low latency, and connectivity. The science behind communication states that the shorter the frequency, the larger the bandwidth.
Hence, 5G networks use shorter frequency (~30 GHz - 300 GHz) and the speed can be as high as 10,000 Mbps, that’s 100 times faster than 4G! In terms of latency, 5G networks top out at 1 millisecond as compared to 200 milliseconds for 4G.
Enhanced broadband services are set to redefine our streaming/browsing experience and are pivotal to the mass-scale deployment of virtual/augmented reality. All major companies have already invested billions in this tech and it has already been deployed in the US, South Korea, and countries in Europe.
5G is set to accelerate industrial transformation, in addition to improved data rates and a hundredfold increase in connected devices paper each unit area which will play a crucial role for IoT transformation and critical communications, it’ll also enable network slicing. Network slicing will allow operators to provide specific portions of their network for different use cases. You can read more about it here.
This provides numerous opportunities for operators in terms of services and customer experience. Hence, with 5G, telecom operators will also play the role of service providers apart from being just distributors.
A crucial ingredient for the success of 5G is Edge Computing, which is basically a distributed computing concept in which information processing and real-time analysis take place at an edge - where the information is consumed.
All of this calls for a change in the approach of the operators. Though they have invested billions in the network infrastructure, 5G supporting devices in the market are quite less, therefore they have to find innovative solutions for higher ROIs till 5G takes all over the globe. One way for effective monetization is to create B2B2X business models where a telecom service provider is primed to deliver services to any number of end-users. Read more about how 5G will innovative services and business models here.
Internet of Things
For the uninitiated, the Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices/things that are connected to the internet. It’s a giant network of connected things that collect and share data tracking their usage and learn from their environment. A simple example would be all smart home appliances such as AC, Microwave, assistants like Echo and Google Home, etc. You can learn more about how they work in this short video by IBM.
As per this IoT analytics report, there will be 11.7 billion IoT devices out of 21.7 billion active connected devices by the end of this year. This figure is expected to almost triple by 2025. IoT is facilitated by the telecom industry both internally and externally, creating potential sources of revenue.
In terms of opportunities, the rising number of IoT devices is directly related to the profits of telecom companies that enable internet connectivity on the go. Moreover, the telcos can themselves become providers of IoT connectivity services for all types of businesses. For example, Vodafone offers IoT solutions for smart grids, vehicle manufacturers, asset management, etc.
These IoT solutions have the power to transform any industry, be it in terms of new revenue channels, improved operational efficiency, IT infrastructure, or better customer engagement and employee efficiency. The telcos themselves are already using the IoT technology to streamline their business and adding value to their own networks. Moreover, they are providing data storage, management, and analysis services for their customers IoT generated data. However, the increasing number of devices also poses the challenge of safe and secure storage of this data.
The future of telcos is set to be disrupted by IoT for sure and they can build separate networks for the platform. The IoT transformation will be sped up by the full-scale deployment of 5G due to its better speed, latency, connectivity, and power usage. Infact, every generation comes with its own set of uses, and 5G has been designed to address the massive IoT phenomenon. The critical communication between these smart devices requires improved performance.
For example, as I wrote in a previous issue on the future of transport, self-driving cars will be very much in use in a decade’s time. These cars would require an effective real-time machine to machine (M2M) communication to navigate through traffic and only a dedicated IoT solution can make that possible.
AI
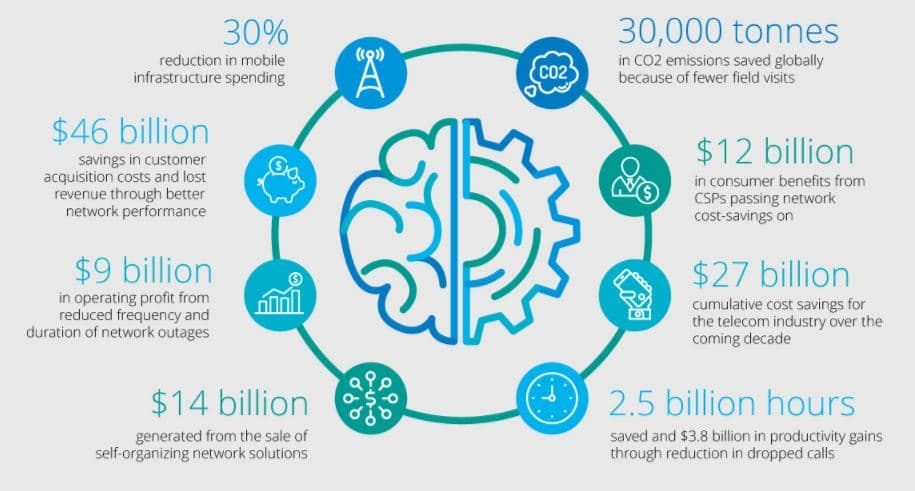
Artificial Intelligence in general is a disruptor for all industries and it’s already playing an important role in the telecom evolution from customer service to network maintenance. Telecom networks are in any way complex and the current transition to cloud and the increase in IoT is going to make things even more complex. Such complexity can be efficiently handled only through AI and ML, reducing the burden on telcos.
Take a look at this infographic about the potential of autonomous networks:
Since the benefits of employing AI in telecom are immense, I’ll discuss them in pointers:
Customer Service: AI will help in personalized customer service analyzing the preferences and interaction with the platform and recommending the best solution that could include the ideal add-on pack. Almost all telcos use virtual assistants and chatbots to respond to their customer’s requests. Checkout Mailmagic that writes an email summary on the go for you in a completely “human” way.
An interesting shift in the future would be towards voice-based assistance thanks to AI and neuro-linguistic processing. All of this leads to better customer satisfaction, reduced churn rate, and faster service.
Network Optimization: Telecoms will switch to service operation centers (SOCs) from network operation centers (NOCs) in the future. SOCs will use AI for closed-loop automation instead of administrators that monitor the network in a NOC. Insights from AI can help monitoring equipment and predicting failures, moreover, they can also allow networks to self-adapt and reconfigure as required. In terms of hardware, AI insights can help to determine where to set up towers/stations and in hardware optimization, reducing performance issues and capital expenditures.
Fraud/Fault detection: ML is instrumental in analyzing any sort of irregular activity such as attacks, theft, fake profiles, viruses. Since they detect these anomalies much quicker than any human counterpart, a crisis can be averted before much damage is done.
Robotic Process Automation: As the name suggests, automation eliminates the need for humans in repetitive processes (for example, billing, document verification, etc.) leading to improved efficiency and errors. This leads to increased customer satisfaction and profitability.
Take a look at some of the top AI startups impacting the telecom industry here.
Wild Disruptor: Space
Remember the fictional Skynet, the villain in the Terminators series. Systems like it are soon going to be a reality in the coming decades, but instead, you’d have a sky full of balloons and drones, mini-sats. These systems would be capable of delivering high-quality broadband services all over the globe, be it any remote area, island, or forest!
Facebook first announced its Project Aquila in 2014 consisting of solar-powered drones with a wingspan of Boeing 737. The idea was to beam internet connectivity to remote areas, but it had to abandon its project after it failed to achieve the long flight times managed by airborne connectivity efforts as compared to its rival, Loon LLC, developed by X, the semi-secret research arm of Google.
Loon, if you haven’t guessed already, is short of a balloon. Google instead of drones were planning to use balloons that’ll hang in the stratosphere to provide high altitude communication technology and bridge the connectivity divide.
After Facebook and Google, enters the innovator aka major disruptor of our generation, Musk!
It took more than 50 years for the landline to get >50% adoption across the world. Infrastructure had a big role to play in the distribution in this case.
The infrastructure was built first which took years to get different regions started with this tech. Later, Internet, cellphone, social media etc. all took off built on top of this infra which was often contested by telecom operators.
This infra is about to become irrelevant just like the telecom companies. This is because the majority of services provided by telecom is being replaced with many OTTs. These OTTs will no longer need the telecoms because they’ve Musk! Yes, UI’m talking about SpaceX’s Starlink project.
Space X’s Starlink whose development began in 2015, has the potential to disrupt the telecom industry completely as we know it, imagine having high-speed internet anywhere and everywhere, who would even use a cellular network for the call then?
Using a series of mini space satellites that weigh only 250 Kgs, they will be delivering high-speed broadband internet to locations where access has been unreliable, expensive, or completely unavailable overcoming all ground infrastructure limitations.
As per their website, Starlink is targeting services in the Northern U.S. and Canada in 2020, rapidly expanding to near-global coverage of the populated world by 2021.
SpaceX has already deployed 60 satellites at a time in September 2020 and aims to deploy 1440 of them that will act as a source of wireless communication and deliver high-speed broadband to us directly on Earth.
While there are concerns over space debris and brilliance (light reflection that could ruin the visible sky), SpaceX has already worked towards them and boasts of an on-orbit debris mitigation system and testing satellites called DarkSat that would be completely undetectable to the naked eye. Read more about its disruption in this Medium article.
This issue is a part of my Futurism series, I wrote about the future of web search, transport, and energy in previous issues. At present, there are a number of trends that can disrupt the telecom industry, telecom providers need to transform with the needs and the fastest way is through partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions.
What we’ll see in the coming five years is a revolution in the approach of telecom operators. We can only wait and watch, the future sure is exciting!
If you found value in this newsletter, consider sharing it with your friends, or subscribe if you haven’t already. Also, I’d love to hear your thoughts in the comments below 👋